Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is not considered a serious disease as such, but it can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life
Osteoarthritis is one of the so-called ‘rheumatic diseases’; These are numerous and varied but have in common the fact that they affect some part of the locomotor system. However, they can be very different in their causes, evolution and treatment.
Osteoarthritis is the most common of all rheumatic diseases. It is characterized by a progressive loss of cartilage in the joints due to wear and tear. This is produced mainly by age although, also, other factors may influence.
This disease is quite common in people over 50 years of age. In fact, according to data from the World Health Organization, approximately 28% of adults over 60 years of age suffer from it. It is estimated that by 2020, this disease will be the fourth cause of disability in the world. Let’s find out all about it together.
Causes of osteoarthritis
The National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases explains that osteoarthritis, also known as ‘osteoarthritis’, occurs when the cartilage in a joint wears down and degenerates. Said cartilage loses elasticity and consistency.
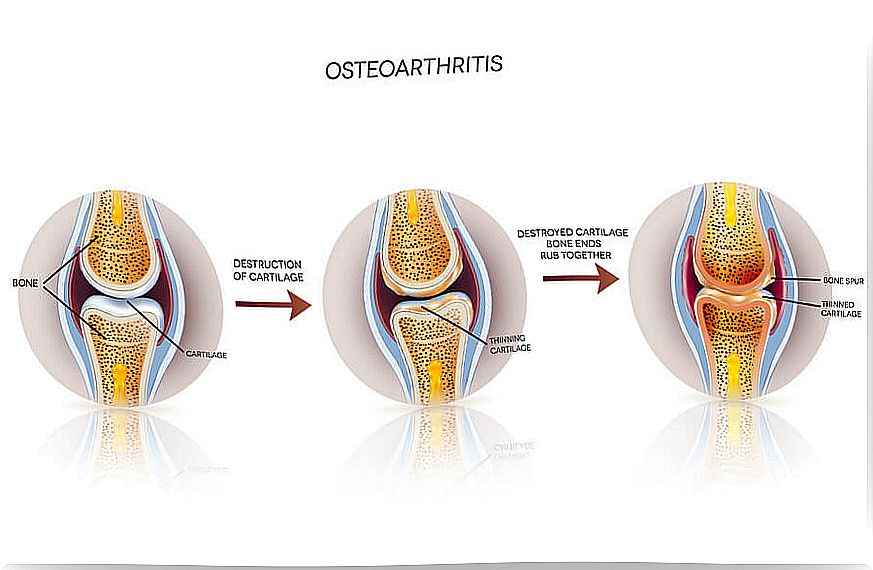
Little by little, it loses its thickness until it practically disappears. When this happens, the ends of the bones are left unprotected and rub against each other.
The affected bones react to this effect. Their response is to become more dense, and then cysts appear within that bone. Also, bone peaks form at the edge of the joint that deforms them.
Different studies have pointed out some factors that could precipitate the onset of osteoarthritis. Next, we mention those exposed on the website of the Arthritis Foundation :
- Age : up to 50 years it is more common in men and, after that age, in women.
- Heredity : Osteoarthritis can appear as a result of an inherited defect in the genes responsible for collagen, one of the components of cartilage.
- Excess physical activity.
- Obesity : it would increase the risk of osteoarthritis in the knees.
- Fractures and injuries.
- Muscle weakness: those with weak quadriceps are more likely to develop this disease in the knees.
Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease that causes severe pain, but with proper treatment, it can be controlled. On the other hand, it is necessary to emphasize that this condition does not necessarily give rise to disabilities or disability in those who suffer from it.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a disease that develops slowly. For this reason, symptoms may go unnoticed at first and become more intense over time. In general, there are five signs that suggest osteoarthritis:
- Joint pain: it is the main symptom. Severe pain is felt in the joints, usually in the knees, hands, or hips.
- Stiffness: the person feels lack of flexibility, especially when getting out of bed or after having been sitting for a long time.
- Swelling and numbness: You can see with the naked eye an inflammation in one or more joints that can lead to numbness.
- Cracking – The patient experiences a ‘rubbing’ or cracking sensation when performing a movement involving the affected joint.
- Discomfort in the knees, feet, hands and hips.
Although pain is the main symptom of osteoarthritis, there are also cases in which it does not appear. Likewise, in this disease, periods of pain alternate with others where it is not manifested.
Types of osteoarthritis and diagnosis
Data from the United States National Library of Medicine indicate that osteoarthritis manifests itself mainly in four areas of the body : knees, hands, hips and spine.
- Knee osteoarthritis is the most common and can be primary or secondary. The first corresponds to the typical form of the disease, while the secondary is due to an injury.
- Osteoarthritis of the hands almost always originates in one joint and then spreads to the others. It often causes deformations and functionality can be impaired.
- Osteoarthritis of the hip generates pain that is located in the inner thigh area, in the groin area or on the outside of the hip.
- Spinal osteoarthritis usually manifests itself in the lumbar or cervical area, although numbness in the extremities can also be perceived.
The diagnosis is usually made after a clinical interview. This is usually complemented by X-rays, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging. Likewise, a high-resolution ultrasound may be indicated to assess the level of progression of osteoarthritis.
Prognosis of the disease
The disease as such is not considered serious, but it could significantly affect the quality of life of the patient. However, the prognosis depends on each particular case. Basically, it derives from the articulation that is compromised and the rate of evolution of the problem.
Early diagnosis and prevention measures can promote a good prognosis. With proper treatment, osteoarthritis progresses more slowly and with less severity.
Treatment is almost always pharmacological or physiotherapeutic aimed at achieving a healthier lifestyle. In some cases, normal measures fail and eventually the need for surgery appears. Generally, with surgery, symptoms are improved and mobility is preserved.
In the presence of joint pain or numbness, it is necessary to consult with the doctor. Only the specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and indicate the best treatment according to the patient’s conditions.